What is Docker ?
Docker is a software platform that allows you to build, test, and deploy applications quickly. Docker packages software into standardized units called containers that have everything the software needs to run including libraries, system tools, code, and runtime. Using Docker, you can quickly deploy and scale applications into any environment and know your code will run.
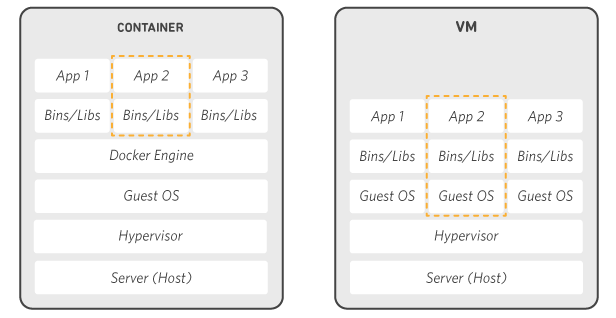
Docker vs Virtualization comparison diagram
- In this post i ll explain how to install docker and configure it
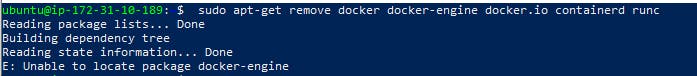
- First we want to remove the old version of docker
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
Output:
- Then update the os
sudo apt-get update
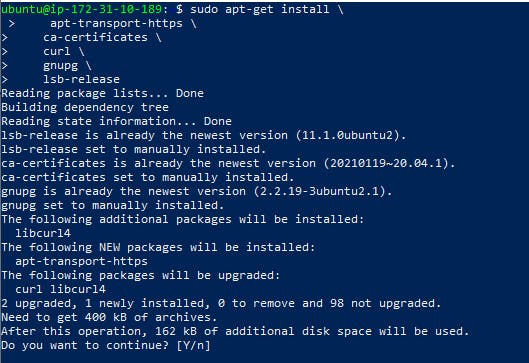
- Install the dependencies
sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg \
lsb-release
Output:
- Add docker official GPG key
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
Output:

- Use the following command to set up the stable repository.
echo \
"deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Output:

- Again update the server
sudo apt-get update
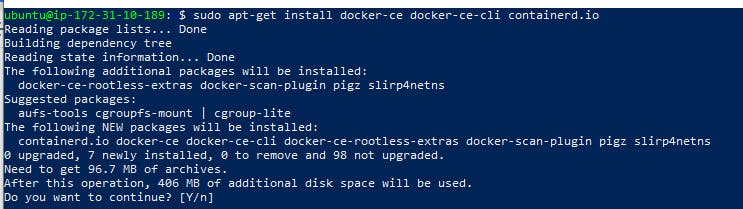
- Install Docker Engine
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Output:
- Now we are add our user in Docker service group. So that we will execute the docker command with out root access or sudo access.
First check the docker group is already created.
sudo cat /etc/group
Output:
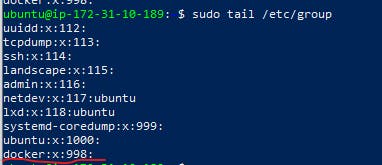
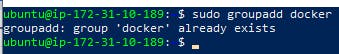
- Now you can see the docker group created inn the last few lines entry. if its not there create the group docker.
sudo groupadd docker
Output:
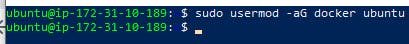
- After that add your non root user to that docker group.
Syntax: sudo usermod −aG docker [non−root user]
sudo usermod −aG docker ubuntu
Output:
- After this enable the docker service on system startup.
Enable Docker service on system startup.
sudo systemctl enable docker.service
sudo systemctl enable containerd.service
Output:

- To take effect all the configuration changes restart the server.
sudo init 6
After that system restart we want to check docker running properly. so that we want to run sample docker container. Docker provide hello world container for testing purpose.
sudo docker run hello-world
This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints a message and exits.
Output:
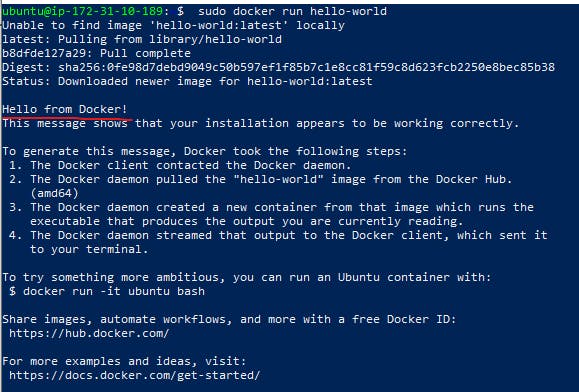
Thats all guys... we are successfully installed docker.
Unsinsatlaion Part
To completely uninstall Docker:
Step 1
dpkg -l | grep -i docker To identify what installed package you have:
Step 2
sudo apt-get purge -y docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce docker-ce-cli sudo apt-get autoremove -y --purge docker-engine docker docker.io docker-ce
The above commands will not remove images, containers, volumes, or user created configuration files on your host. If you wish to delete all images, containers, and volumes run the following commands:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker /etc/docker sudo rm /etc/apparmor.d/docker sudo groupdel docker sudo rm -rf /var/run/docker.sock
You have removed Docker from the system completely.
