What is LINUX
Linux is the open source operating system.
Just like Windows, iOS, and Mac OS, Linux is an operating system. In fact, one of the most popular platforms on the planet, Android, is powered by the Linux operating system. An operating system is software that manages all of the hardware resources associated with your desktop or laptop. To put it simply, the operating system manages the communication between your software and your hardware.
- Linux Have the different folder structure compare with windows.
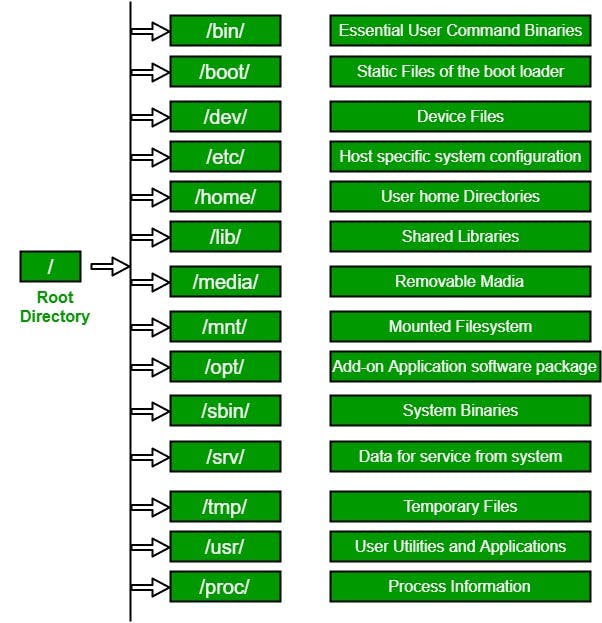
Find the below image. its basic structure for all Linux based OS.
Here I have explained some basic linux commands.
- Create folder in Linux
syntax : mkdir folder1
mkdir project1
- List out the files and folder in current location
ls
- Want to show including hidden files and folders
ls -la
- To know the where you are currently in terminal present working directory
pwd
- To delete the files and folders
Syntax: rm -r file or folder name
rm -r file1
rm -r folderlinux
To install any package in linux
- In Redhat or Centos
yum install package name
Example
yum install httpd
- In Debian based and ubuntu
apt install package name
Example
apt install nginx
- To start stop restart or check the status for any service
- There is two commands systemctl and service.
- Service is older version of OS and systemctl is newer one. The main think is both are different syntax
- For example in the systemctl package name is middle and the status or restart is last. in the other hand service command status or start stop is middle and service name is last.
For Example
systemctl status httpd
service httpd status
- To check status
service nginx status
- To restart the service
systemctl restart nginx
service nginx restart
- To stop the service or start the service
systemctl start httpd
service httpd start
- Other one important command is sudo . its like windows command run as administrator.
also sudo command record the activity.
Example:
sudo vi /etc/hosts
In the above command normal user cannot edit the host file in the etc location.root user only have write access to that file.
So in this situation we will use sudo command.
- To create the user account in linux
Syntax : useradd username
Example:
useradd shivam
- To set the password for the created user account
Syntax: passwd username
passwd shivam
Its prompted password and again verify the password.
- To login to the user
Syntax: su username
(su means switch user)
Example:
su shivam
- To verify ur user is created check it in passwd file last few lines.
cat /etc/passwd
To Check Free disk space
df -h
To Copy files same location .
Syntax: cp source_file target_file
cp file.txt file2.txt
To Copy files from one location to other location.
Syntax: cp /sourcefile_location/source_file_name /targetfile_location/target_file_name
cp /home/ubuntu/index.php /var/www/html/index.html
TO Recursively copy all the files.
To copy a directory, including all its files and subdirectories, to another directory, enter (copy directories recursively):
cp -R * /home/ubuntu/new/
- TO Rename the file or folder
Syntax: mv old_filname new_filename
Example
mv venket.txt venketnew.txt
mv old_foldername newfolder name
To Delete the file and folder
Syntax: rm -r file or folder name
rm -r 1.txt
rm -r dryfold
